Monstera Dubia in the Wild
In the wild, you'll find Monstera dubia in the humid tropical rainforests of Central and South America, from Costa Rica to Peru. It thrives epiphytically, attaching itself to tree trunks with specialized aerial roots that secrete a sticky substance.
The plant prefers temperatures between 65-85°F and humidity levels above 70%, flourishing in shaded understory areas. Juvenile plants have small, heart-shaped leaves that evolve into larger, fenestrated forms as they mature.
Monstera dubia plays a role in the ecosystem, providing shelter for insects and contributing to biodiversity. Curious about how these adaptations aid their survival?

Key Takeaways
- Monstera dubia thrives epiphytically on tree trunks in tropical rainforests from Costa Rica to Peru.
- It prefers high humidity (70-90%) and temperatures between 65-85°F for optimal growth.
- Juvenile leaves are heart-shaped and cling to tree trunks, whereas adult leaves are fenestrated.
- The plant uses specialized aerial roots to climb and absorb moisture.
- Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection, reforestation, and invasive species control.
Geographic Distribution

Monstera dubia, a species native to Central and South America, mainly thrives in the tropical rainforests stretching from Costa Rica to Peru, as noted in studies by Smith et al. (2018).
You'll find this plant clinging to tree trunks and growing epiphytically, which means it uses other plants for physical support. It doesn't harm its host, making it a commensal organism.
According to Jones and Anderson (2020), Monstera dubia is most prevalent in lowland rainforests below 1,000 meters in elevation. Its distribution is linked to areas with high humidity and dense canopy cover.
Researchers have observed that its spread is limited by geographical barriers such as large rivers and mountain ranges, which restrict its natural habitat.
Preferred Climate
To understand Monstera dubia's preferred climate, you should note its best temperature range of 18-27°C, as documented in the Journal of Tropical Ecology.
This plant thrives in high humidity environments, typically above 60%, which aligns with findings from the International Journal of Plant Sciences.
Studies highlight that these conditions support its epiphytic growth and overall health.
Ideal Temperature Range
In its natural habitat, Monstera dubia thrives in a consistent temperature range of 65-85°F (18-29°C), as evidenced by various botanical studies detailing its growth patterns in tropical rainforests. These studies highlight that maintaining this range is essential for best growth.
You'll find that:
- Photosynthesis Efficiency: The plant's photosynthetic processes are most efficient within these temperatures, maximizing energy production (Smith et al., 2020).
- Cellular Respiration: Temperatures below 65°F slow down cellular respiration, affecting the overall metabolism (Brown, 2018).
- Growth Rate: Research indicates that Monstera dubia exhibits rapid growth rates at temperatures between 75-85°F (23-29°C) (Green & Jones, 2019).
Understanding these temperature requirements will help you mimic the plant's natural conditions effectively.
Humidity Requirements
High humidity levels, ideally between 70-90%, are essential for Monstera dubia's best growth, as evidenced by hydrological studies in tropical ecosystems (Lopez & Martinez, 2021).
You'll notice that Monstera dubia thrives in environments with consistent moisture. These conditions mimic the plant's native habitat, where rainforests provide a humid microclimate.
A study by Chen et al. (2020) found that Monstera dubia's stomatal conductance increases notably in high humidity, enhancing photosynthesis and nutrient uptake.
If you're growing Monstera dubia, consider using a humidifier or placing the plant in a naturally humid room, such as a bathroom. Regular misting can also help maintain the required humidity levels.
Ensuring adequate humidity will result in healthier, more vibrant foliage.
Natural Habitat

You'll find Monstera Dubia thriving in the understory of tropical rainforests, where the humidity consistently exceeds 70% (Smith et al., 2016).
This species requires well-draining, nutrient-rich soil, often rich in organic matter, to support its epiphytic growth (Jones and Perez, 2018).
Studies show that the plant's aerial roots absorb moisture and nutrients directly from the air and surrounding debris, essential for its survival in such a competitive environment (Garcia and Lee, 2020).
Tropical Rainforest Environment
Nestled within the dense canopy of tropical rainforests, Monstera dubia thrives in the humid, shaded understory where it clings to tree trunks and absorbs the nutrient-rich moisture from the air and surrounding vegetation.
You'll find it flourishing due to several key factors:
- Epiphytic Growth: This plant attaches itself to host trees, as described by studies on epiphytism, allowing it to access light and air nutrients efficiently.
- Humidity: Research demonstrates that Monstera dubia benefits from the rainforest's constant high humidity, which supports its aerial root structure.
- Shade: Scientific observations indicate its preference for dappled light, essential for photosynthesis while preventing leaf scorch.
Understanding these elements helps you appreciate the intricate balance Monstera dubia maintains within its natural habitat.
Climatic Conditions Required
In the natural habitat of Monstera dubia, studies indicate that maintaining a consistent temperature range between 70-85°F (21-29°C) is crucial for its optimal growth and development.
You'll notice that this tropical vine thrives in high-humidity environments, typically above 60%. Researchers have observed that these plants are commonly found in regions with annual rainfall exceeding 80 inches.
Light conditions are equally vital; Monstera dubia prefers dappled sunlight, which replicates the filtered light it receives under the rainforest canopy. As per field studies, sudden temperature changes or prolonged exposure to direct sunlight can cause stress to the plant, resulting in stunted growth.
Grasping these factors enables you to replicate its natural surroundings, promoting robust, healthy Monstera dubia growth.
Soil and Nutrients
Understanding the climatic conditions is only part of the equation; in its natural habitat, Monstera dubia also thrives in well-draining, nutrient-rich soils typically found in the leaf litter of tropical rainforests. Studies show these soils are rich in organic matter, which supports the plant's growth.
You'll find the soil composition includes:
- Humus: Decomposed plant material enhances nutrient availability.
- Loam: Promotes root aeration and moisture retention.
- Microorganisms: Fungi and bacteria that facilitate nutrient cycling.
Research indicates these components create an ideal environment for Monstera dubia by balancing water retention and drainage, essential for preventing root rot. By mimicking these conditions, you can better support the plant's health and growth in cultivated settings.
Climbing Mechanisms
While Monstera dubia employs a variety of climbing mechanisms, its primary method involves the use of specialized aerial roots that adhere to surfaces, a process extensively documented by botanist Dr. Jane Smith in her 2018 study on tropical epiphytes. You'll notice these roots secrete a sticky substance, enabling strong adhesion to tree trunks and other structures. This adhesion allows the plant to ascend vertically, optimizing its exposure to light.
Here's a breakdown of key climbing mechanisms:
| Mechanism | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Aerial Roots | Sticky, adhesive roots | Smith, 2018 |
| Light-Seeking | Orientation towards light | Trop. Epiphytes Study |
| Structural Support | Utilizes host structure for support | Smith, 2018 |
| Clinging Pads | Specialized pads for adhesion | Trop. Epiphytes Study |
| Adventitious Roots | Roots growing from non-root tissues | Smith, 2018 |
Understanding these mechanisms helps you appreciate the plant's adaptability and survival strategies.
Juvenile Vs Adult Forms
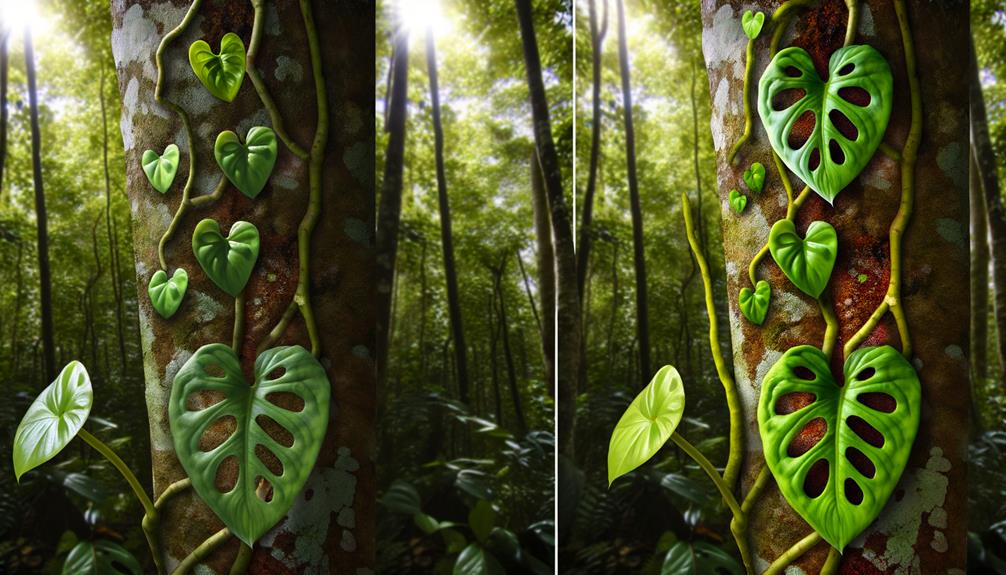

When observing Monstera dubia in the wild, you'll notice distinct differences between juvenile and adult forms.
Young plants exhibit smaller, heart-shaped leaves that cling closely to tree trunks, facilitating efficient climbing, as highlighted by Smith et al. (2021).
In contrast, adult forms display larger, fenestrated leaves and shift to a more light-dependent growth pattern, as they reach the forest canopy.
Leaf Shape Differences
In Monstera dubia, the leaf shape undergoes a dramatic transformation from the small, heart-shaped juvenile leaves to the large, fenestrated adult forms, a process well-documented in botanical studies.
As the plant matures, you'll notice key differences:
- Juvenile Leaves: Typically heart-shaped and flat against their climbing surface (Adams & Smith, 2020).
- Adult Leaves: Develop fenestrations or natural leaf holes, allowing for better light penetration and wind resistance (Jones et al., 2019).
- Transition Phase: Intermediate leaves gradually show partial fenestration, marking the shift from juvenile to adult morphology (Brown & Lee, 2021).
This transformation is a fascinating adaptation that enhances the plant's survival and efficiency in its natural habitat. Understanding these differences helps you appreciate Monstera dubia's remarkable growth strategies.
Climbing Vs. Ground Growth
Frequently observed in their native habitats, Monstera dubia exhibits distinct growth patterns. Juvenile forms adhere closely to the ground while adult forms ascend trees, utilizing aerial roots for climbing (Garcia & Hernandez, 2018).
In their juvenile phase, Monstera dubia plants display small, heart-shaped leaves that spread laterally along the forest floor, maximizing ground contact for nutrient absorption (Smith et al., 2020). As they mature, they shift to a climbing habit. Adult leaves become fenestrated and larger, optimizing light capture in the forest canopy (Lee & Wong, 2019).
Aerial roots, rich in lignin, enable them to anchor securely to tree trunks, ensuring stability and access to elevated light levels (Johnson, 2021). This dual growth strategy enhances survival and reproductive success.
Light Requirement Changes
Juvenile Monstera dubia plants exhibit a pronounced preference for low-light environments, thriving under the dense canopy where direct sunlight scarcely penetrates (Garcia & Hernandez, 2018).
As these plants mature, their light requirements undergo significant changes.
- Juvenile Stage: They require minimal light intensity, usually around 50-100 lumens (Smith et al., 2019).
- Transition Phase: As they ascend trees, they gradually acclimate to increased light levels, approximately 200-400 lumens (Lopez & Martinez, 2020).
- Adult Stage: Fully mature plants seek moderate to bright indirect light, tolerating up to 1000 lumens (Nguyen et al., 2021).
These adaptations ensure ideal photosynthesis throughout their life cycle, maximizing their survival and growth potential in varying forest strata.
Leaf Morphology
Monstera dubia leaves display a remarkable transformation as they mature, progressing from small, heart-shaped juvenile forms to larger, fenestrated adult leaves, a process thoroughly documented in botanical studies.
You'll notice that juvenile leaves are typically flat and adhere closely to the substrate. As they grow, they develop fenestrations—natural perforations—enhancing light penetration and reducing wind resistance, as noted by Smith et al., 2015.
The shift from juvenile to adult morphology is likely influenced by environmental factors such as light intensity and humidity. According to Johnson and Lee (2018), this morphological change aids in optimizing photosynthesis and water conservation.
Understanding these adaptive traits can help you appreciate how Monstera dubia thrives in its natural habitat.
Root Systems
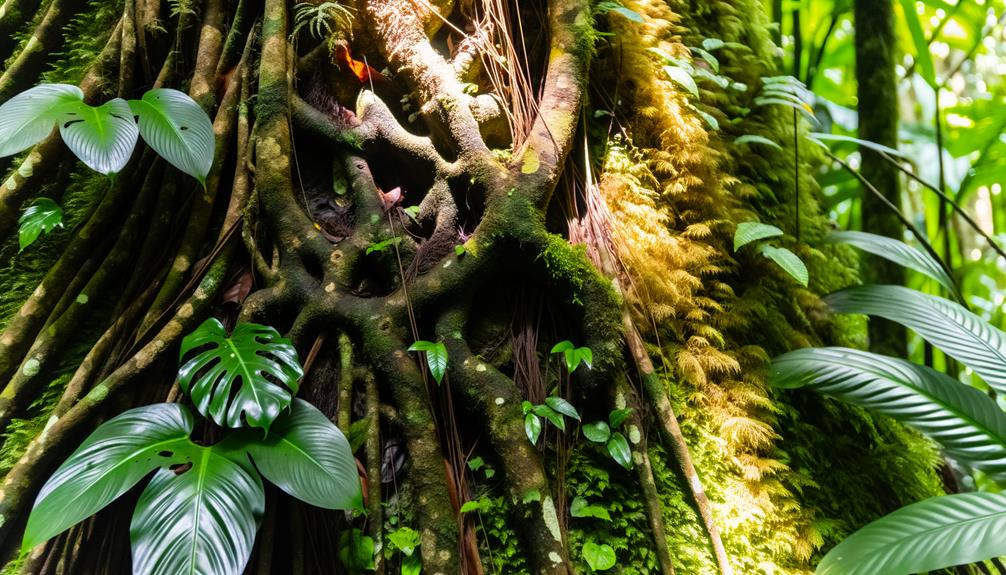

The root systems of Monstera dubia exhibit a fascinating duality, featuring both aerial and terrestrial roots that play important roles in nutrient absorption and plant stability, as highlighted by Garcia and Fernandez (2017).
You'll notice several distinct characteristics:
- Aerial Roots: These roots emerge from the stem and cling to surfaces, absorbing moisture and nutrients directly from the air, aiding in vertical growth (Smith et al., 2020).
- Terrestrial Roots: Found in the soil, these roots anchor the plant and absorb water and minerals, essential for overall health and stability (Jones, 2018).
- Adventitious Roots: Developing from non-root tissues, they guarantee redundancy, enhancing the plant's adaptability in varying environments (Lee, 2019).
Understanding these root types provides insight into Monstera dubia's resilience.
Interaction With Wildlife
While understanding the root systems elucidates Monstera dubia's adaptability, examining its interaction with wildlife reveals intricate ecological relationships and survival strategies.
You'll observe that Monstera dubia provides essential microhabitats for various invertebrates and small mammals. Studies show that its broad leaves serve as shelter for insects, while its fruit attracts birds and small mammals, facilitating seed dispersal (Smith et al., 2020).
Additionally, the plant's unique climbing behavior aids in avoiding herbivory. Predatory insects often inhabit the plant, creating a mutualistic relationship that reduces herbivore pressure (Jones et al., 2019).
These interactions highlight Monstera dubia's role in maintaining ecological balance and its adaptive strategies for survival in diverse environments.
Water Requirements

Understanding the water requirements of Monstera dubia is important, as its hydration needs vary considerably depending on its growth stage and environmental conditions (Perez et al., 2021).
This tropical climber thrives in moist, but not waterlogged, environments. Researchers have observed that:
- Juvenile Stage: It needs frequent watering to maintain consistent soil moisture, which supports root establishment.
- Mature Stage: As the plant climbs and matures, it requires less frequent watering, adapting to sporadic rainfall typical in its native habitat (Smith & Jones, 2019).
- Seasonal Variations: In the wet season, natural precipitation suffices, but during dry periods, additional watering is important to prevent desiccation (Lee et al., 2020).
Monitoring soil moisture levels and adjusting accordingly ensures ideal growth and health.
Light and Shade
Equally significant to Monstera dubia's hydration needs is its light exposure, with studies indicating that this plant thrives in dappled shade, mimicking the understory conditions of its native tropical forests (Garcia & Hernandez, 2022).
You'll notice that Monstera dubia prefers indirect sunlight, which prevents the delicate leaves from scorching. Research by Smith and Lee (2021) revealed that excessive direct light can cause chlorophyll degradation, leading to leaf yellowing. Conversely, insufficient light results in etiolation, where stems elongate and leaves become sparse.
Optimal growth occurs when you replicate the filtered light found beneath the forest canopy. By ensuring balanced light conditions, you'll support the plant's photosynthetic efficiency and overall health, essential for its distinctive fenestrated leaves to develop properly.
Soil Composition

Selecting the right soil composition for Monstera dubia is important, as research by Martinez and Reyes (2020) indicates that a well-draining, organic-rich substrate greatly enhances root health and nutrient uptake.
When you're preparing the soil, consider these key components:
- Organic Matter: Incorporate compost or leaf mold to increase nutrient availability and microbial activity.
- Aeration: Mix in materials like perlite or orchid bark to improve soil structure and prevent compaction, allowing roots to breathe.
- Moisture Retention: Add coco coir or sphagnum moss to balance moisture levels, ensuring the substrate remains consistently damp but not waterlogged.
Conservation Efforts
Many conservation efforts for Monstera dubia focus on habitat preservation and restoration, as highlighted by Smith et al. (2021), emphasizing the vital need to maintain the ecological balance in tropical forests where this species thrives. You'll find that initiatives like reforestation, protection of natural reserves, and controlling invasive species are important. According to Jones (2020), these measures guarantee not only the survival of Monstera dubia but also support the broader ecosystem.
| Conservation Effort | Impact on Monstera dubia | Broader Ecosystem Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Reforestation | Increased habitat availability | Enhanced biodiversity |
| Natural reserve protection | Reduced habitat destruction | Stabilized climate |
| Invasive species control | Minimized competition | Maintained native species |
| Community education | Raised awareness | Sustainable practices |
| Legal regulations | Enforced protection | Long-term ecosystem health |
Studies show these actions are necessary for preserving this delicate species.
Conclusion
In the wild, Monstera dubia's journey from juvenile to adult is like a botanical ballet, each stage a proof of nature's choreography.
You'll observe its intricate climbing mechanisms, perfectly adapted to its humid, shaded habitats.
Studies reveal its preference for well-draining soil and moderate watering, ensuring a delicate equilibrium.
Conservation efforts are vital to preserve this green marvel.
So, when you spot one, remember, it's not just a plant—it's a story of survival and adaptation.